The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has taken a significant step in the battle against inflation by raising the repo rate by 25 bps (basis points) to 6.5%.
The central bank uses the repo rate, a crucial monetary policy tool, to regulate the money supply in the economy. This latest increase aims to curb inflation and maintain stability.
Slight History
A crucial tool for the central bank’s monetary policy, the repo rate, has experienced several adjustments recently. The repo rate in June 2019 was 5.75%. It experienced multiple falls and ascents throughout the ensuing years.
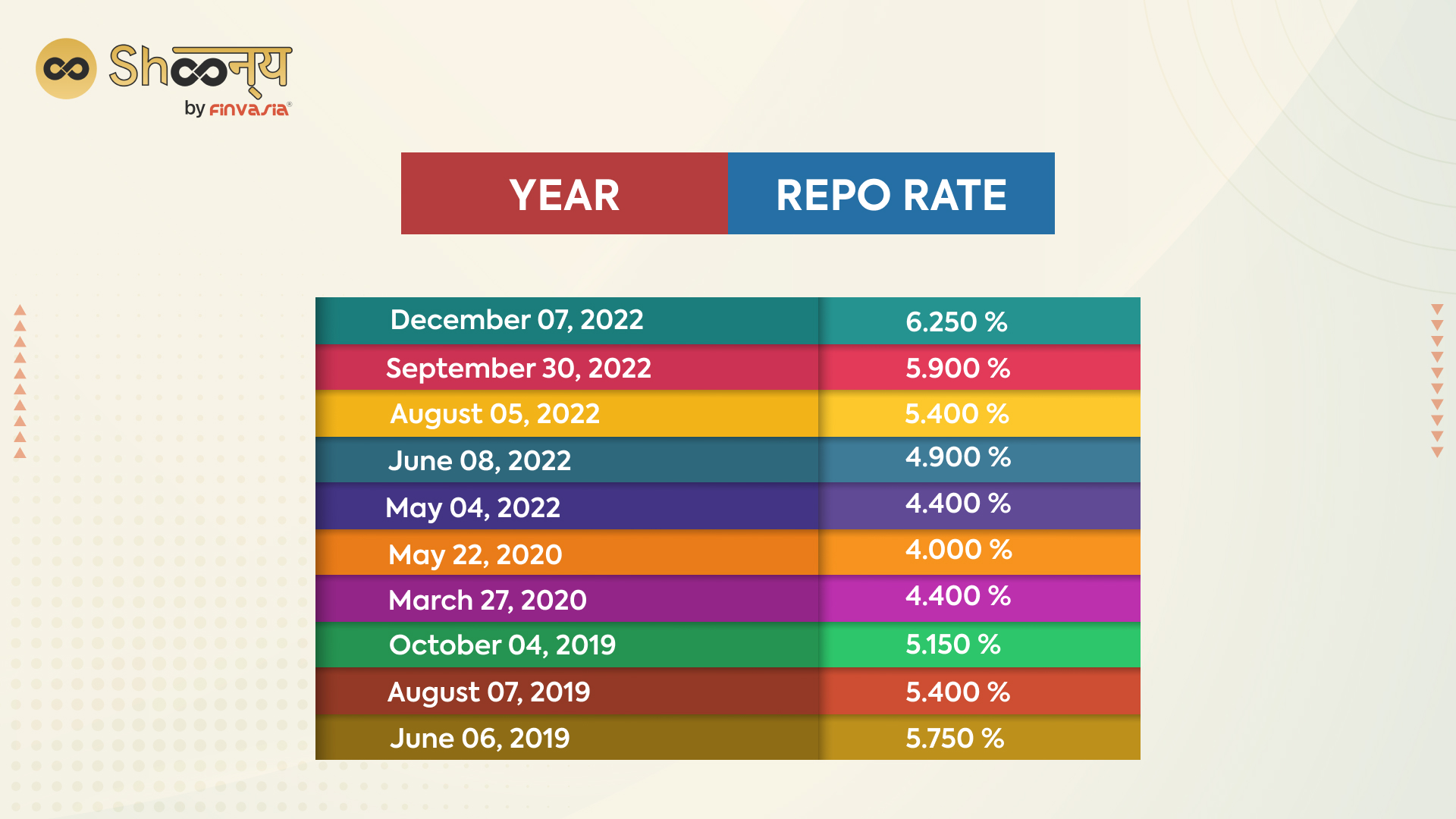
Compared to the period before the outbreak of COVID-19 in March 2020, the repo rate has increased by 2.5%. During the pandemic, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) reduced the repo rate to stimulate the economy by putting more money into the hands of the public.
However, in light of the recent hikes in inflation and the fiscal deficit status of the economy, as outlined in the 2023 budget, the RBI has decided to raise the repo rate to limit the money supply in the economy.
Who had taken the decision?
The hike in repo rate was decided by the RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC), comprising six members, including the Governor- Shaktikanta Das.
The rise was necessitated by the persistent increase in inflation, as measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI). The CPI has consistently remained above the target set by the RBI, leading the central bank to take action to control price rises and ensure economic balance.
Impact on businesses and individuals
There will be both good and negative effects of the repo rate increase on the economy.
On the flip side, it will make borrowing more expensive for both firms and people, which could hamper economic growth.
It will also promote saving and deter extravagant expenditure, thus assisting in the control of inflation.
Impact on traders and investors
Traders and investors will also be affected by the repo rate hike. The increased borrowing costs will decrease demand for stocks and bonds, potentially causing a price fall. However, the long-term impact of controlling inflation will be positive for the economy and the markets.
Impact on small and medium-sized enterprises
The repo rate hike will particularly impact small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and the unorganised sector. The rise in borrowing costs will pressure their margins and reduce their competitiveness.
The RBI must strike a balance between controlling inflation and supporting the growth of these sectors.
Impact on the housing sector
The housing sector will also feel the effects of the repo rate hike. The increase in borrowing costs will result in a rise in home loan interest rates, making homes less affordable for buyers. This could lead to a drop in demand for housing and a slowdown in the real estate sector.
Sources: economictimes.indiatimes.com
______________________________________________________________________________________
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks, read all the related documents carefully before investing.