India now ranks as the fourth largest stock market in India. But, have you ever wondered who keeps a watchful eye over India’s bustling stock market? SEBI – the Securities and Exchange Board of India it is. From safeguarding investor interests to shaping the future of corporate governance, this regulatory powerhouse handles it all. It ensures fairness and transparency in India’s dynamic economy. But what is SEBI, and who owns it and what is the role of SEBI in the stock exchange market?
Let us take a look.
What is SEBI?
SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India)- An Overview
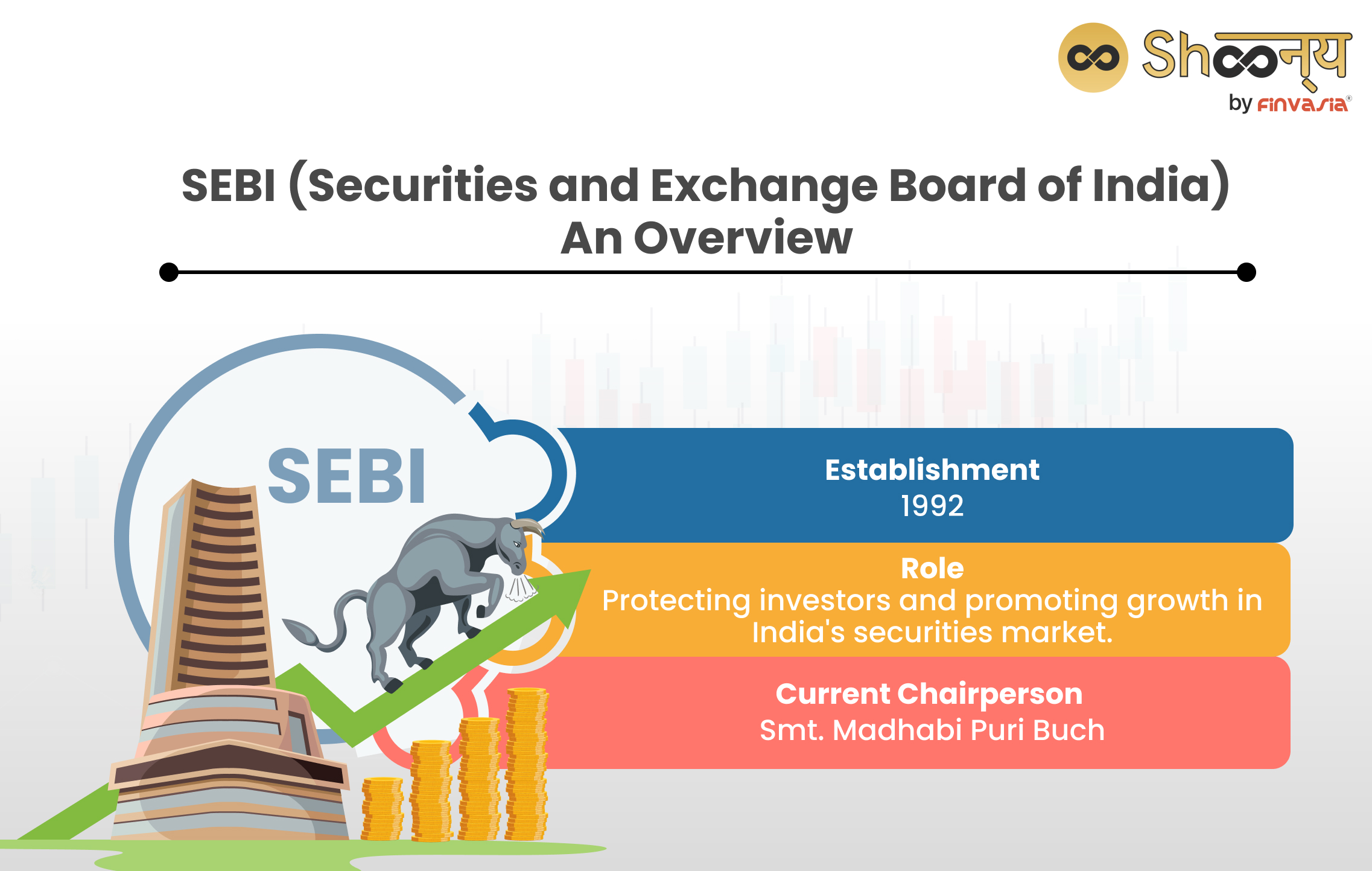
| Basis | Information |
| Full form | Securities and Exchange Board of India |
| Establishment | 1992 |
| Role | Protecting investors and promoting growth in India’s securities market |
| Current Chairperson | Smt. Madhabi Puri Buch |
SEBI stands for the Securities and Exchange Board of India.
It’s the regulatory body responsible for overseeing the securities markets in India.
SEBI’s main goal is to safeguard the interests of investors and boost the development of the securities market.
History of SEBI
The Government of India constituted the Securities and Exchange Board of India as a non-statutory body on April 12, 1988.
Later, SEBI became a statutory body in 1992. This came with the enactment of the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act (15 of 1992) on January 30.
SEBI’s Charter
According to its charter, SEBI is expected to be responsible for three main groups:
- The issuers of securities
- Investors
- Market intermediaries
The role of SEBI is to protect the interests of investors in securities.
It aims to ensure transparency in the Indian stock market.
- SEBI actively ensures fairness and efficiency in stock market operations.
- It regulates intermediaries and participants to safeguard investor interests.
- SEBI actively promotes investor education and awareness to foster a robust investment environment.
What is the Role of SEBI in Stock Exchange?
The Securities and Exchange Board of India plays a substantial role in the Indian stock market:
- SEBI diligently oversees stock exchange operations to maintain market integrity.
- It enforces stringent rules to curb market manipulation and insider trading.
- SEBI vigilantly monitors listed companies’ adherence to disclosure norms, thereby promoting transparency.
Exploring the Objectives of SEBI
- Protecting the interests of investors in securities remains paramount for SEBI.
- SEBI strives to foster the development and regulation of the securities market.
- Ensuring the orderly and healthy growth of the securities market stands as a key objective.
SEBI Functions and Powers
The Securities and Exchange Board of India’s basic functions, as described in its preamble, are:
- To protect investors’ interests in securities.
- Promote the evolution of the securities market.
- Regulate the market along with related matters.
Here are the functions of SEBI in the stock exchange market of India:
• Regulatory Functions
These include registration and regulation of intermediaries such as:
Stockbrokers
Sub-brokers
Share transfer agents
Bankers to an issue
Registrars to an issue, merchant bankers, trustees of trust deeds, etc.
It also includes regulation of collective investment schemes, venture capital funds, credit rating agencies, etc.
• Developmental Functions
SEBI promotes market development, such as conducting research, training and education programs.
The main intent is to create awareness among investors and provide assistance to issuers and intermediaries, etc.
• Protective Functions
SEBI provides guidelines and codes of conduct, audits intermediaries, and adjudicates to ensure investor protection.
It also imposes penalties for violations, initiates prosecution and enforcement actions, etc.
- SEBI meticulously registers and regulates market intermediaries, including brokers and sub-brokers.
- It rigorously monitors securities markets to prevent malpractices and maintain market integrity.
- SEBI maintains the market discipline.
Conclusion
SEBI is an important regulator of the securities market in India. It performs a dual objectives of protecting investors and promoting market development. If you are planning to open a demat account and begin trading, you can do it tension-free. SEBI plays a vital role in ensuring transparency and fairness in stock market trading.
FAQs| What is SEBI?
SEBI is managed by its board of members, consisting of the Chairman nominated by the Union Government of India, two members from the Union Finance Ministry, one member from the Reserve Bank of India, and five members nominated by the Union Government, with at least three being whole-time members.
SEBI generates revenue from various sources, including fees and charges from intermediaries, issuers, and investors, grants and loans from the central government, income from investments, and penalties and fines for violations.
The main role of SEBI is to protect investors’ interests in securities and promote the overall development of the securities market in India.
______________________________________________________________________________________
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks; read all the related documents carefully before investing.

