This blog will help you understand multiple aspects of trading in the Forex Market or currency market in India, along with specific terminologies, processes, regulations and the risks involved in currency trading.
The currency and currency market is integral to the global financial system. They play a crucial role in facilitating international trade and investment, as well as in determining the exchange rates between different currencies.
For example, the Indian Rupee is the currency used in India, while the US Dollar is the currency used in the United States. Each currency has its own unique symbol and is typically abbreviated using three letters, such as INR for Indian Rupee or USD for US Dollar.
Standard Terms related to Currency Market and Currency Trading
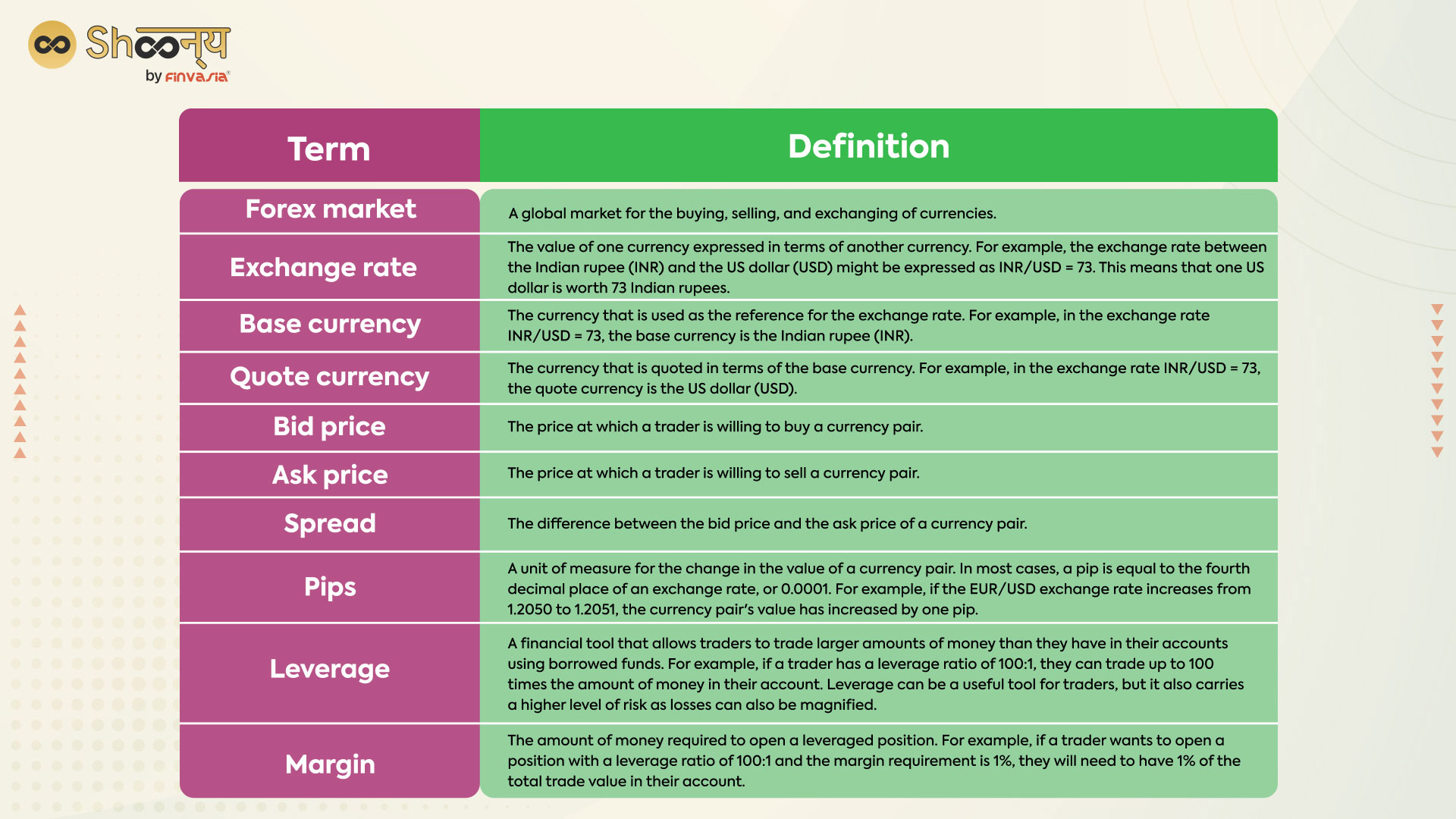
Decentralized markets where currencies are traded are known as currency markets or foreign exchange markets (Forex). Foreign Exchange, commonly referred to as Forex or FX, is the exchange of one currency for another. With a daily turnover of over $5 trillion, it is the largest financial market in the world. Traders and investors worldwide can access the Forex market 24 hours a day, five days a week.
I have heard a lot about Forex Trading.
But are Forex Trading and Currency Trading the same thing?
Forex trading refers specifically to the buying and selling of different currencies in the Forex market, intending to profit from changes in exchange rates. Currency trading, on the other hand, is a broader term that refers to the exchange of one currency for another, whether for purposes of speculation or as part of a financial transaction.
For example, if you are a tourist travelling to the United States and you need to exchange Indian Rupees for US Dollars, you are engaging in currency trading. However, if you are a trader buying and selling US Dollars and Euros in the Forex market to profit from exchange rate changes, you are engaging in Forex trading. Forex Trading is not yet popular among investors because they seem afraid of one thing i.e. if Forex trading is legal in India. The short answer is yes; Forex trading is legal in India, but it is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
Legality Concern with Forex Trading In India
How do I legally participate in Forex trading in India?
As a trader, you must open an account with a registered broker and comply with the regulations set by the RBI and SEBI.
Regulation by FEMA, RBI, and SEBI for forex trading in India
Forex trading in India is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), and the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA). Here is a summary of the regulatory framework for Forex trading in India:
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI): The RBI is the central bank of India and is responsible for managing the country’s monetary policy and regulating the financial system. In relation to Forex trading, the RBI sets the guidelines for foreign exchange transactions and oversees the activities of Forex brokers in India.
- Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI): The SEBI is the regulatory body for the securities market in India and is responsible for protecting the interests of investors. In relation to Forex trading, the SEBI ensures that Forex brokers are registered and compliant with the necessary regulations.
- Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA): FEMA is legislation that regulates foreign exchange transactions in India. It sets out the rules and regulations for the purchase and sale of foreign exchange, as well as the reporting requirements for certain types of transactions.
Note: Traders need to be aware of these regulatory requirements to ensure that their Forex trading activities are legal and compliant in India.
Now, when we talk of Currency Trading, we suggest you be aware of the potential risks (leverage, inflation, change in exchange rates, etc.) involved to help ensure you don’t lose your money.
It is important for traders and investors to understand the risks associated with currency trading and to manage their risk exposure appropriately. This may involve using risk management strategies such as stop-loss orders, diversifying their portfolio, and only risking an amount of capital that they can afford to lose.
Why does the Indian Rupee Appreciate or Depreciate?
But how and why does the Currency or Indian Rupee appreciates or depreciates? Why do these risks actually rise?
Here are some key factors that can cause the Indian Rupee to appreciate or depreciate:

- Economic conditions: The strength of the Indian economy can impact the value of the Indian Rupee. If the economy is growing and performing well, the value of the Rupee may appreciate due to increased demand for the currency. Conversely, if the economy is experiencing a downturn, the value of the Rupee may depreciate.
- Interest rates: Interest rates can also impact the value of the Indian Rupee. If the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the country’s central bank, raises interest rates, it can increase demand for the Rupee as investors seek higher returns. This can cause the value of the Rupee to appreciate. On the other hand, if the RBI lowers interest rates, it may lead to a decrease in demand for the Rupee and a depreciation in its value.
- Political stability: Political stability and the credibility of the Indian government can also impact the value of the Rupee. Political uncertainty or instability can lead to a decrease in demand for the Rupee and a depreciation in its value.
- Inflation: Inflation, or the general increase in prices of goods and services over time, can also impact the value of the Rupee. If the inflation rate in India is higher than in other countries, the Rupee value may depreciate, as it takes more units of the currency to purchase the same goods and services.
By understanding these factors and monitoring economic and political developments, traders and investors can make informed decisions about the value of the Indian Rupee and the potential for appreciation or depreciation.
Now, this is all about the Indian Currency.
Exotic Currencies
But have you heard about the concept of Exotic currencies?
They are currencies that are not commonly traded on the global foreign exchange (Forex) market and are considered to be more risky and volatile than major or minor currencies. Exotic currencies are typically associated with emerging or developing economies and may not be as widely accepted or traded as major currencies, such as the US Dollar, the Euro, or the Japanese Yen.
Some examples of exotic currencies include
- The Turkish Lira
- The Brazilian Real
- The South African Rand
- The Mexican Peso
- The Indonesian Rupiah
You know the stock market in India is subject to market fluctuations, and the same goes for currency and currency markets. Currency exchange risk, also known as foreign exchange (Forex) risk, applies here, which is the potential for losses due to changes in the exchange rates of different currencies.
When we talk about trading currency, exotic currency pairs tend to be more volatile and less liquid than major currency pairs, making them riskier to trade. However, they can also offer higher potential returns for traders willing to take on the added risk.
Sources of Currency Exchange Risk
- Transaction risk: This refers to the risk that a company or individual may face when they make a financial transaction denominated in a foreign currency.
For example, suppose a company exports goods to a foreign country and is paid in foreign currency. In that case, it is exposed to transaction risk if the value of that currency declines before the company can convert it into its home currency.
- Translation risk: This refers to the risk that a company or an individual may face when they need to translate the financial statements of a foreign subsidiary or investment into their home currency.
If the value of the foreign currency changes during the translation process, it can result in a gain or loss for the company or individual.
- Economic risk: This refers to the risk that a company or individual may face due to changes in the economic conditions of a foreign country.
For example, if a company has operations in a foreign country and the value of that country’s currency declines due to an economic downturn, the company may face financial losses.
To manage currency exchange risk, companies and individuals can use a variety of strategies, including hedging, diversification, and currency forward contracts.
Basic Strategies to Follow
Are you planning to try your luck in currency trading? Then, don’t forget to follow these basics of trading in the currency market:
There are several things to consider when trading in the currency market in India.
- Regulatory framework: Currency trading in India is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI). It is important for traders to be aware of the regulatory requirements and to ensure that their trading activities are legal and compliant.
- Broker selection: It is important to choose a reputable and regulated broker when trading in the currency market in India. Look for brokers that are registered with the RBI and SEBI, and check for any negative reviews or complaints.
- Risk management: Trading in the currency market carries a high level of risk due to its leveraged nature. It is important for traders to carefully manage their risk exposure and to use risk management strategies, such as stop-loss orders, to protect against potential losses.
- Trading strategy: Developing a well-thought-out trading strategy can help traders make informed decisions about when to buy and sell currencies. This may involve using technical analysis, fundamental analysis, or a combination of both.
- Tax implications: It is important for traders to be aware of the tax implications of currency trading in India. Capital gains from currency trading are taxed at the individual’s applicable tax rate, which varies based on their income level.
How do I compare the Indian currency with other Currencies of the World?
You know,
To compare the exchange rate of the Indian Rupee with other world currencies, you can use an online currency converter or check the exchange rates quoted by banks and financial institutions. It is also possible to compare the relative values of different currencies using purchasing power parity (PPP) and understand the Tips for Currency Exchange to clearly measures the number of goods and services that can be purchased with a given amount of currency.
However, we suggest you follow the Best currency tips to ensure a safe currency trading experience.
FAQs
You can invest in the Indian stock market’s currency market by using currency derivatives, such as futures and options, available on NSE and BSE. These tools enable you to speculate on the future price of currency pairs like USD/INR.
In the Indian stock market, you’ll find three currency markets: the National Stock Exchange (NSE), the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE), and the Metropolitan Stock Exchange of India Ltd (MSEI). These markets let you trade currency derivatives tied to pairs like USD/INR, EUR/INR, GBP/INR, and JPY/INR.
The currency market in the Indian stock market is where people trade money through currency derivatives. These are like agreements to exchange one currency for another at a certain rate and date in the future. It’s a bit like making promises about money.
In the Indian stock market, four key types of currency markets include spot markets, forward markets, futures markets and options markets.

