How do companies like Amazon, Tata, Walmart, and Starbucks expand their businesses to different countries and regions? How do they acquire the resources, technology, and expertise to operate in diverse markets? The answer is foreign direct investment (FDI). Foreign direct investment (FDI) is a key driver of global economic integration and development. It allows companies and governments to access new markets, technologies, and opportunities. But what are the different types of FDI? How does FDI affect the host and home countries and their economies?
Let us take a look.
What is FDI- Foreign Direct Investment
Foreign Direct Investment, or FDI, is when a company or individual from one country invests in a business or assets located in another country. This is different from buying stocks or bonds of a foreign company in the stock market. FDI involves actually owning and controlling a part of that business.
FDI is a form of cross-border investment. It involves establishing a lasting interest and control in a foreign enterprise.
Imagine you’re from India, and you decide to open a tech startup in the United States. That’s an example of Foreign Direct Investment or FDI. You’re directly investing your money and resources into a business in another country.
FDI can happen for various reasons.
It might be because a company sees potential for growth in a foreign market like the US. It wants to tap into a more developed tech ecosystem. Or it seeks to access a larger pool of skilled workers available in that foreign location.
What is the Role of FDI
Foreign direct investment contributes to the economic development and growth of both the investor and the host countries. FDI facilitates the transfer of technology, knowledge, and skills across borders. FDI enhances the competitiveness and innovation of firms and industries. FDI fosters the cooperation of countries in regional and global value chains. FDI also influences the political, social, and environmental aspects of the countries involved.
Types of FDI (Foreign Direct Investment)
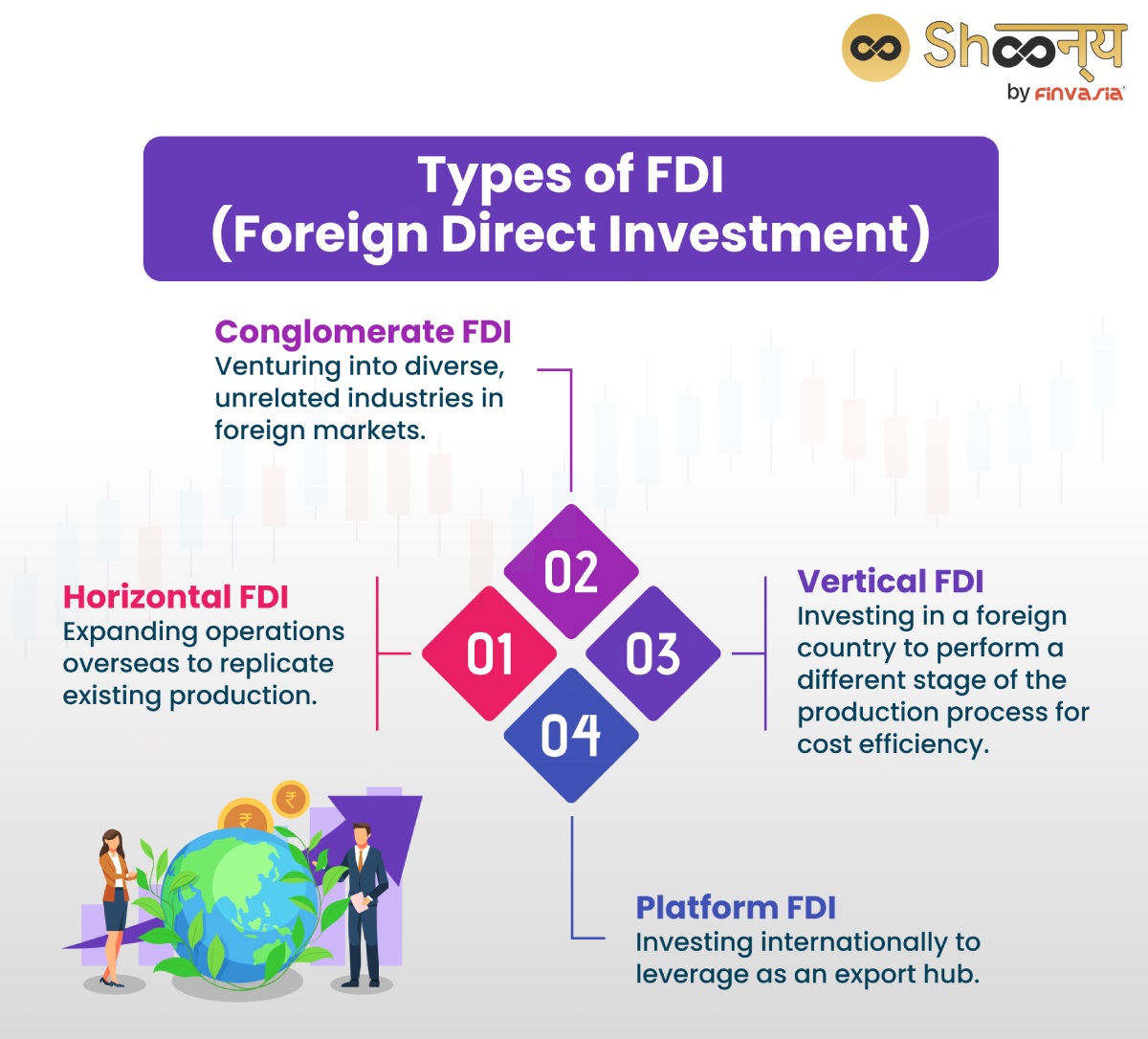
- Horizontal FDI: When a company expands its operations to a foreign country to produce the same goods/services it produces domestically.
For example, an Indian smartphone company sets up a factory in China to manufacture phones. - Vertical FDI: Here, a company invests in a foreign country to perform a different stage of the production process.
For instance, an Indian textile manufacturer invests in a cotton farm in the United States to secure a raw material source.
- Conglomerate FDI: When a company expands its business into areas that are unrelated to its current line of business.
For example, an Indian automobile manufacturer invests in a chain of hotels in Australia. - Platform FDI: When a company invests in a foreign country for the production /distribution of its products or services.
For instance, an Indian e-commerce company establishes warehouses and logistics networks in the United Kingdom. It is done with the aim of expanding user reach.
Foreign Direct Investment Examples
- Automobile Manufacturing
Imagine a Japanese car manufacturer decides to build a new factory in India. It aims to produce vehicles specifically for the Indian market. They would invest money into acquiring land, constructing the factory, buying equipment, and hiring workers. This investment is a direct investment by a foreign company into the Indian economy. - Technology Sector
Suppose a Silicon Valley tech company decides to establish an R&D centre in Bangalore, India. They invest funds to set up the facility, hire local talent, and conduct research to develop new products or improve existing ones. This investment brings capital into India. Also, it transfers technology and knowledge, contributing to the growth of the Indian tech industry.
Advantages of FDI
FDI plays a huge role in the overall economy
- Economic Growth: FDI stimulates economic growth by bringing in capital, technology, and expertise from foreign countries.
- Increased Employment: FDI can create job opportunities in the host country, reducing unemployment rates.
- Technology Transfer: It involves the transfer of advanced technologies and managerial practices. This helps in boosting productivity and competitiveness.
- Infrastructure Development: Foreign investors may contribute to the development of infrastructure such as roads, ports, and utilities.
- Export Promotion: FDI can lead to increased exports. As a result, foreign-invested firms may produce goods/ services on a large scale.
Disadvantages of FDI
Despite its multifaced pros, FDI has certain drawbacks, too:
- Heavy reliance on FDI can make the host country vulnerable to fluctuations in foreign investment flows.
- There’s a risk that foreign investors may exploit local resources or labour. This leads to economic inequality or environmental degradation.
- Excessive FDI may result in loss of control over key industries or strategic assets. It can raise concerns about national sovereignty.
- Foreign companies may outcompete local firms,. This may lead to market dominance and reduce diversity in the economy.
- Profits generated by foreign-invested enterprises may be repatriated to their home countries.
Result?
It reduces the amount of capital reinvested in the host country’s economy.
Conclusion
Foreign direct investment (FDI) serves as a vital mechanism for global economic integration. It offers avenues for technological transfer, job creation, and infrastructure development. However, while FDI presents numerous advantages, it also brings forth challenges like dependency on foreign investors and potential exploitation. Striking a balance between harnessing the benefits of FDI and mitigating its drawbacks is important. This benefits both home and host countries.
FAQs | Foreign Direct Investment
FDI or Foreign Direct Investment is an investment made by a foreign entity in a business or project in India. FDI is a source of non-debt finance, technology transfer, and economic growth for India.
Overseas direct investment (ODI) is an investment made by an Indian entity in a business or project outside India. ODI is a way of expanding the global presence, accessing new markets, and acquiring resources and expertise for Indian entities.
The two most known types of FDI are horizontal and vertical FDI. Horizontal FDI is when a foreign entity establishes the same type of business operation in another country as it operates in its home country. Vertical FDI is when a foreign entity invests in a different stage of the production process in another country than it does in its home country.
______________________________________________________________________________________
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks; read all the related documents carefully before investing.

