IPOs are one such category that is talked about by almost everyone these days. But there’s another term you might not be as familiar with: FPO. FPO and IPO are two ways companies raise funds from the public by issuing shares. But what exactly is an FPO in the stock market? How is it different from an IPO?
Let’s take a look!
What is FPO in the Share Market?
FPO stands for Follow-on Public Offer.
It is a process of issuing additional shares to the public by a company that is already listed on a stock exchange. It is the secondary offering of shares by a listed company to existing or new investors.
- FPO is different from IPO, which is the first time a company offers its shares to the public.
- It is a way for a company to raise more capital, reduce debt, or change its shareholding pattern.
- FPO in the share market can affect the share price, earnings per share, and market capitalisation of the company.
- It can also provide an opportunity for investors to buy shares of a company at a discounted price.
What is FPO: Explore the Basics
- FPO stands for Follow-on Public Offering, where companies already listed on the stock market issue more shares to the public.
- It’s a way for companies to raise extra money from investors to fund projects like expansion or debt reduction.
- Dilutive Follow On Public Offerings increase the total number of shares, potentially diluting existing shareholders’ ownership.
- Non-dilutive FPOs involve existing shareholders selling their shares to the public without the company issuing new ones.
- Follow-On Public Offers can offer opportunities for both new and existing investors to participate in a company’s growth journey.
An example of an FPO in the Indian market could be when a well-known company, let’s say XYZ Ltd., decides to expand its operations by building new factories or entering new markets. To raise funds for this expansion, XYZ Ltd. decides to issue additional shares to the public through Follow-On Public Offers.
Investors who acknowledge the company’s growth potential may buy these new shares, contributing to the funds needed for expansion.
This Follow-On Public Offer allows existing shareholders to maintain their ownership percentage in the company while providing an opportunity for new investors to participate in XYZ Ltd.’s growth journey.
What is the Difference between FPO and IPO?
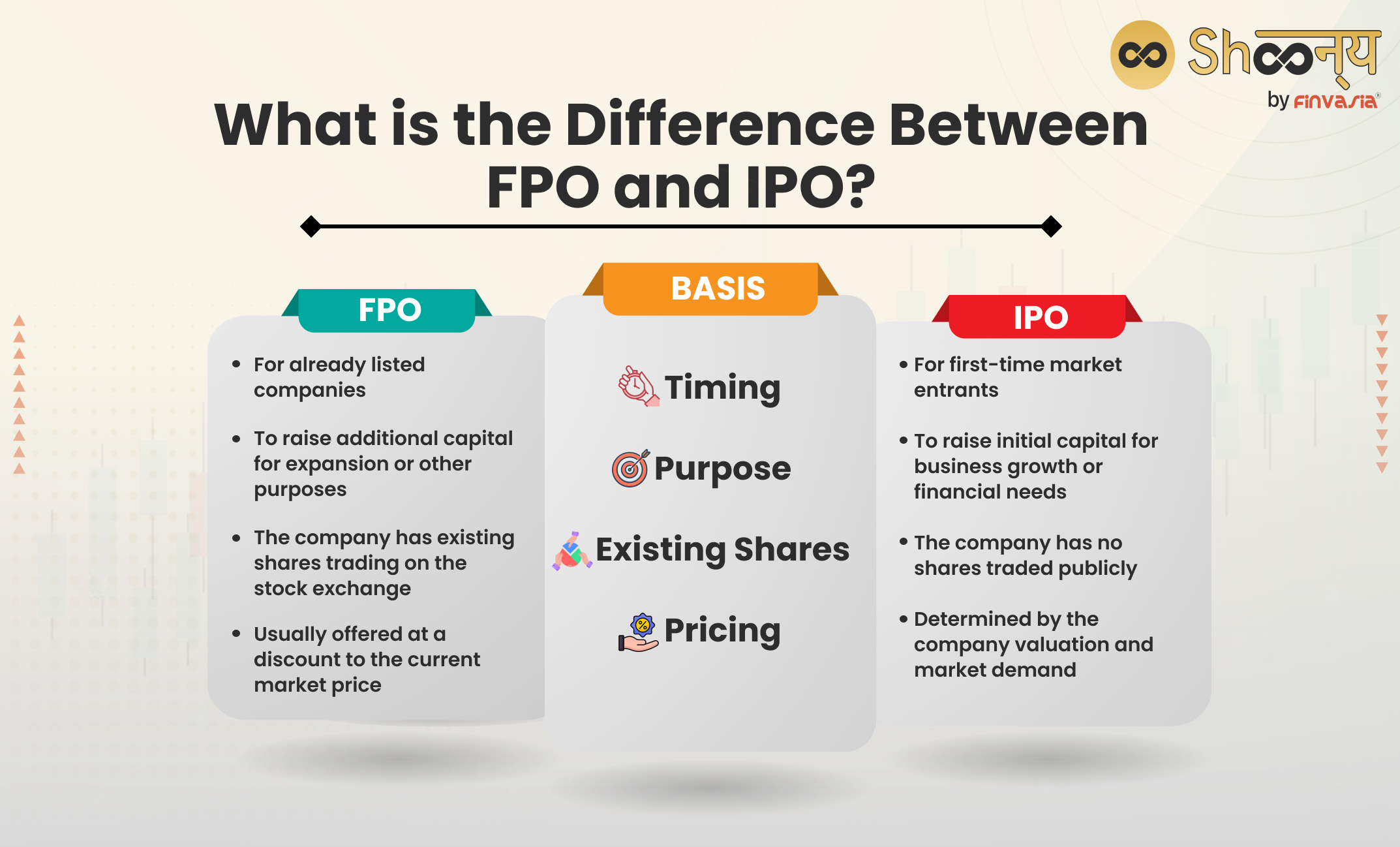
| Basis | FPO (Follow-on Public Offering) | IPO (Initial Public Offering) |
| Timing | Issued by already listed companies | Issued by companies entering the market for the first time |
| Purpose | Raise additional capital for expansion or other purposes | Raise capital for business expansion or to meet financial needs |
| Existing Shares | The company already has shares trading on the stock exchange | The company doesn’t have any shares traded publicly |
| Pricing | Often offered at a discount to the current market price | Usually priced based on company valuation and market demand |
| Investor Base | Open to existing shareholders and new investors | Open to institutional and retail investors |
The main difference between an FPO and an IPO is that a company that is already listed on a stock exchange conducts Follow-On Public Offers. On the other hand, with an IPO, the company goes public for the first time.
Some of the other differences between FPO and IPO are:
• Follow-on public offers help raise additional capital or reduce debt, while IPOs help raise initial capital or expand the business.
• Follow-On Public Offer is based on the current market price of the shares, while IPO is based on the valuation of the company.
• FPO is less risky and less costly than IPO, as the company has already established its reputation and track record in the market.
• Also, Follow-On Public Offers are less attractive and less profitable than IPOs, as the company has already diluted its earnings and shareholding.
Types of FPO (Follow-on Public Offering) in the Share Market
There are two main types of Follow-On Public Offers:
Dilutive FPO
This occurs when a company issues new shares to the public, increasing the total number of shares outstanding. It can dilute earnings per share and the ownership of existing shareholders. Dilutive FPOs are typically undertaken to fund expansion, diversification, or debt reduction.
Non-dilutive FPO
In this scenario, existing shareholders sell their shares to the public without the company issuing new shares. While the company doesn’t receive proceeds from this type of FPO, it allows existing shareholders to monetise their investments.
FPO (Follow-on Public Offering) Benefits
FPO can have various benefits for the company and the investors, such as:
• It can help the company raise more capital, improve its financial position, and enhance its growth prospects.
• It can also aid the company to reduce its debt burden, lower its interest cost, and improve its credit rating.
• Follow-On Public Offers help the company increase its public shareholding, broaden its investor base, and improve its liquidity and marketability.
• Lastly, Follow-On Public Offers can help investors buy shares of a company at a lower price than the market price and benefit from the future appreciation of the shares.
• FPO can help investors to diversify their portfolios, reduce their risk, and increase their returns.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, an FPO, or Follow-on Public Offering, is a way for already-listed companies to raise additional capital. Contrary to an IPO, an FPO occurs after a company is already trading on the stock exchange. Understanding the basics, types, and benefits of FPOs can help you choose the right investment type!
FAQs| FPO in the Share Market
FPO stands for Follow-on Public Offer. It is the issuance of shares by a company that is already listed on a stock exchange. A company may undertake an FPO to raise additional capital, reduce debt, or change the shareholding pattern.
Investing in FPOs can have some advantages and disadvantages. They’re generally less risky because the company is already established. However, they can dilute existing shareholders’ earnings and ownership.
To invest in FPOs, you need to have a Demat account, a trading account, & a bank account. You can apply for FPOs through an online trading platform.
______________________________________________________________________________________
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks; read all the related documents carefully before investing.

