Managing personal finance is a crucial skill for a secure financial future. Let’s explore practical strategies and principles that will help you navigate the world of personal finance, even if you’re just starting out.
Personal Finance Guide: Navigating Your Financial Journey
Think of a personal finance guide as your roadmap to financial success. It’s your go-to resource for understanding key concepts like budgeting, saving, investing, and debt management. For example, if you’re saving for a dream vacation, a personal finance guide will help you break down the steps needed to reach that goal.
Types of Personal Finance: Building a Strong Foundation
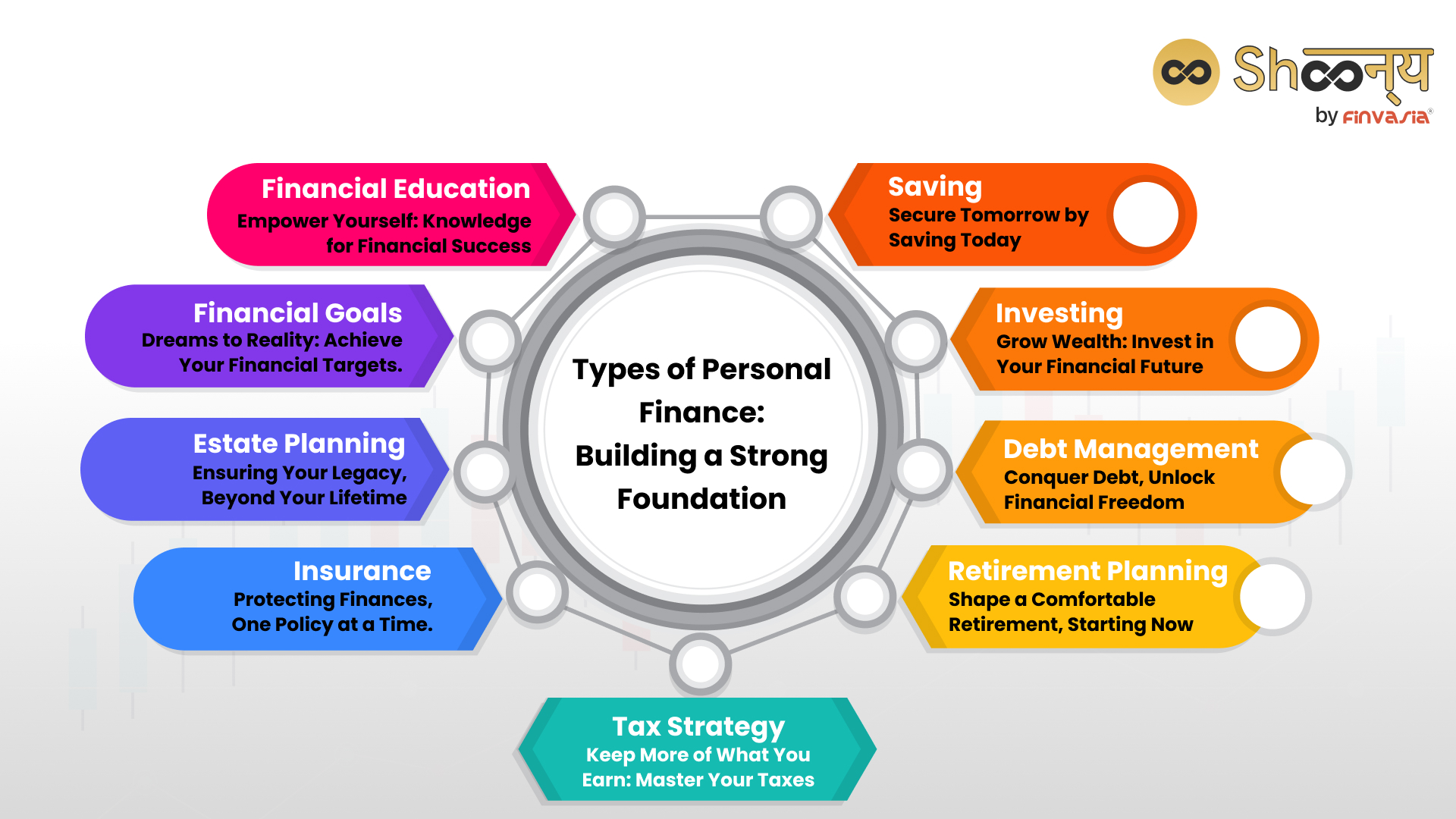
Personal finance types encompass different aspects, each contributing to your financial well-being. Budgeting involves creating a spending plan to control your expenses. Saving acts as a safety net for unexpected situations, like medical emergencies. Investing helps your money grow over time, such as putting funds into a diversified portfolio. Debt management ensures you handle loans and credit responsibly, preventing unnecessary financial strain.
- Budgeting: Budgeting is about planning how you’ll use your money wisely. For example, if your monthly income is ₹40,000 and your expenses include rent (₹15,000), groceries (₹5,000), transportation (₹3,000), and entertainment (₹2,000), creating a budget helps you allocate ₹25,000 for necessities and ₹15,000 for discretionary spending, ensuring you stay within your means.
- Savings: Saving is the foundation of financial security. Suppose you’re saving for a vacation. By setting aside ₹2,000 every month, you’ll have ₹24,000 in a year to fund your trip.
- Investing: Investing is putting your money to work to potentially earn more. Imagine investing ₹10,000 in shares of a reputable Indian company. If the stock appreciates by 15% in a year, your investment would be worth ₹11,500.
- Tax Planning: Tax planning involves using legal strategies to reduce your tax liability. For instance, you can invest in tax-saving instruments like the Equity-Linked Savings Scheme (ELSS) to lower your taxable income.
- Retirement Planning: Planning for retirement is crucial. Contributions to schemes like the Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF) or the Public Provident Fund (PPF) over time can build a substantial retirement nest egg.
- Debt Management: Efficiently managing loans is essential. If you have a high-interest personal loan, consider using savings or windfalls to pay it off faster and save on interest.
- Insurance: Insurance protects against financial risks. Health insurance, for instance, can help cover costly medical bills during illnesses or accidents.
- Estate Planning: Estate planning ensures your assets are distributed as per your wishes after your passing. Drafting a will can prevent potential disputes among heirs.
- Financial Goals: Setting clear financial goals helps you prioritize your spending and saving. If your goal is to buy a car, determine how much you need and create a savings plan to achieve it.
- Emergency Funds: Unforeseen expenses, such as medical emergencies or car repairs, can disrupt your finances. An emergency fund, equivalent to three to six months’ living expenses, provides a financial safety net during challenging times.
These fundamental personal finance concepts empower individuals in India to make informed financial decisions, attain financial security, and reach their financial aspirations. Properly managing these areas can lead to a more stable and prosperous financial future.
Money Management Tips: Practical Strategies for Success
When it comes to handling your finances wisely, practical strategies can make a world of difference. One such strategy is what’s known as the 50-30-20 rule. It’s a straightforward way to allocate your income for better financial stability:
Let’s say you earn Rs. 50,000 each month. According to this rule, you should divide your income into three categories:
- 50% for Essentials: This chunk, which amounts to Rs. 25,000 in your case, should be set aside for vital expenses like rent or mortgage payments, groceries, utility bills, and transportation costs. These are the necessities that keep your life running smoothly.
- 30% for Non-Essentials: This category, which equals Rs. 15,000 for you, is for discretionary spending. It covers things like dining out, entertainment, hobbies, and shopping – basically, the activities that make life enjoyable. It’s important to strike a balance here to ensure you have room for both fun and responsible spending.
- 20% for Savings and Debt Repayment: The remaining 20%, which comes to Rs. 10,000 in your case, should be directed towards securing your financial future. This can include building an emergency fund, saving for retirement, or paying off debts. It’s a crucial step in ensuring your long-term financial well-being.
By adhering to the 50-30-20 rule, you can effectively manage your money. It ensures that you cover your essential needs, enjoy life sensibly, and work towards your financial objectives. Remember, consistency and discipline in following this approach are key. Over time, it can lead to a more secure and prosperous financial future.
Money Management Tips for Students: Navigating Student Life
As a student, managing money is crucial. Create a budget that includes tuition, books, and living costs. Take advantage of student discounts to save on essentials like books and software. Consider part-time jobs or freelance work to supplement your income. For instance, if you’re studying medicine, you could offer tutoring services to fellow students in subjects you excel at.
Personal Finance for Beginners: Taking the First Steps
Embarking on your personal finance journey as a beginner requires understanding some fundamental steps. Let’s break it down into manageable actions:
- Expense Tracking: Start by keeping tabs on your spending. You can make use of tools like MoneyTrack or even a basic spreadsheet. Categorise your expenditures to gain insights into your financial habits.
- Exploring Investments: Don’t be intimidated by the world of investments. Even if you have a modest sum to begin with, there are beginner-friendly options. Consider starting with fixed deposits or mutual funds. These offer lower risks and are accessible for those just starting out.
Example: You could kickstart your investment journey with a Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) of Rs. 1,000 per month. Over time, this consistent approach can lead to significant growth. As your financial situation improves, you can consider increasing your SIP contributions.
- Financial Education: Invest in your financial knowledge. There are numerous resources available, from books to online courses and financial seminars. The more you learn about personal finance, the better equipped you’ll be to make informed decisions.
- Seek Professional Advice: When in doubt or dealing with complex financial situations, consider consulting a financial advisor. They can provide personalised guidance tailored to your specific financial circumstances and goals.
Remember, personal finance is a journey, and it’s perfectly normal to start small. The key is taking those initial steps and committing to continuous financial growth and improvement. With dedication and time, you’ll build a solid foundation of financial expertise and security, bringing your financial dreams closer to reality.
In Conclusion
Managing personal finance is a journey that involves understanding different facets and making informed decisions. By following the strategies and concepts outlined in this beginner-friendly guide, you’ll be on your way to financial stability and achieving your goals. Remember, everyone starts somewhere, and taking these steps today will have a positive impact on your financial future.
FAQs| How To Manage Personal Finance
The four key rules of personal finance involve budgeting, saving, investing, and managing debt.
Personal financial management generally involves assessing your financial situation, setting goals, creating a budget, implementing the plan, and regularly reviewing and adjusting as needed.
The main areas of personal finance encompass income, expenses, savings, investments, and debt management.
Personal finance is often categorised into earning, spending, saving, investing, and protecting.
Personal finance consists of income, expenses, savings, investments, debt, insurance, and retirement planning.
The 50-30-20 rule suggests allocating 50% of your income to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings and debt repayment.
______________________________________________________________________________________
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks; read all the related documents carefully before investing.

