Did you know that companies have an alternative to IPOs for raising capital? Have you heard about the term ‘OFS in share market?’ It involves the sale of existing shares by promoters or large shareholders without raising new capital. IPOs, on the other hand, represent a company’s first stock sale to the public. While both present investment opportunities, they come with distinct characteristics. OFS vs IPO, how do they actually differ and which is better?
Let’s learn!
What is OFS in Stock Market?
OFS full form- Offer for Sale
An Offer for Sale (OFS) is a method used by promoters or existing shareholders of a listed company to sell their shares to the public.
Introduced by India’s securities market regulator SEBI in 2012, it’s a simpler and faster alternative to a Follow-on Public Offer (FPO).
OFS in stock market means offering the shares already owned. It’s like selling something you own to someone else, but in this case, it’s shares of a company.
So, when you hear about OFS in IPO, it means current shareholders are selling their shares to investors like you.
Let’s understand the OFS meaning with an example!
Suppose Mr Rao, a prominent shareholder in Swiggy, decides to cut his stake by 10%. Instead of listing these shares on the open market, he opts for an Offer for Sale in IPO. Now, what will happen?
This will allow retail and institutional investors to buy these shares at a fixed price.
The OFS method is particularly favoured for its efficiency and ability to quickly adjust the promoter’s holding to meet regulatory requirements.
Key highlights of the Offer for Sale- OFS in stock market, as outlined in the SEBI circular
- Eligibility:
OFS facility is available on the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and National Stock Exchange (NSE).
- Size of Offer:
Minimum offer size of ₹25 crores, but can be less to achieve minimum public shareholding.
- Advertisement and offer expenses:
The seller bears all expenses related to OFS.
- Risk Management:
The clearinghouse collects 100% of the order value in cash from non-institutional investors.
However, an upfront margin is required for bid modification/cancellation.
- Allocation
A minimum of 25% of shares are reserved for mutual funds and insurance companies.
Start investing in over 3000 direct mutual funds with a free Demat account and zero brokerage!
No single bidder (excluding mutual funds and insurance companies) allocated more than 25% of the offer size.
How OFS Works (OFS Process)
Only promoters or shareholders holding more than 10% of the share capital can initiate an OFS.
- Seller Decision:
Existing shareholders (like company founders or investors) decide to sell some of their shares to the public. - Announcement:
The selling shareholders must announce the Offer for Sale (OFS) through the stock exchange. This should involve the details of how many shares they want to sell and the minimum price. - Bidding Period:
Investors can place bids for the shares during a specified time. This indicates how many shares they want and the price they are willing to pay, as long as it meets the minimum price. - Allocation:
After the bidding ends, the shares are allocated to the highest bidders. This allocation is based on their offers and order sizes. - Settlement:
Once shares are allocated, the buyers’ accounts are charged for the shares. With this, the sellers receive the proceeds. - Ownership Change:
Ownership of the shares transfers from the sellers to the new buyers without affecting the company’s total shares since no new shares are created.
What is an IPO?
An Initial Public Offering (IPO) is when a company decides to sell its shares to the public for the first time. It is the process by which a private company becomes publicly traded by offering its shares to the public.
This capital can be used for expansion, paying off debt, or other corporate purposes.
It’s like a company’s debut on the stock market.
How IPOs Work
The company decides it needs to raise money for growth by selling shares to the public.
- Hiring Underwriters:
The company selects investment banks who act as underwriters. They help to manage the overall IPO process, pricing and legal requirements. - Financial Preparation:
The company prepares important financial documents (called the Draft Red Herring Prospectus or DRHP) to show its financial status and future plans. - Regulatory Approval:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) reviews the DRHP to ensure it meets legal standards and provides accurate information. - Pricing
The company and underwriters set a price for the shares and then the IPO opens for the public. - Subscription Period:
Investors have a specific time to place orders to buy shares at the IPO price. - Allotment of Shares:
Shares are distributed to investors based on their orders and the overall demand. - Listing on Stock Exchange:
The company’s shares are listed on a stock exchange, making them available for trading.
What is the Key Difference Between IPO and OFS?
An IPO involves a private company issuing new shares to the public to raise fresh capital. OFS in the share market involves existing shareholders selling their shares without raising new capital for the company.
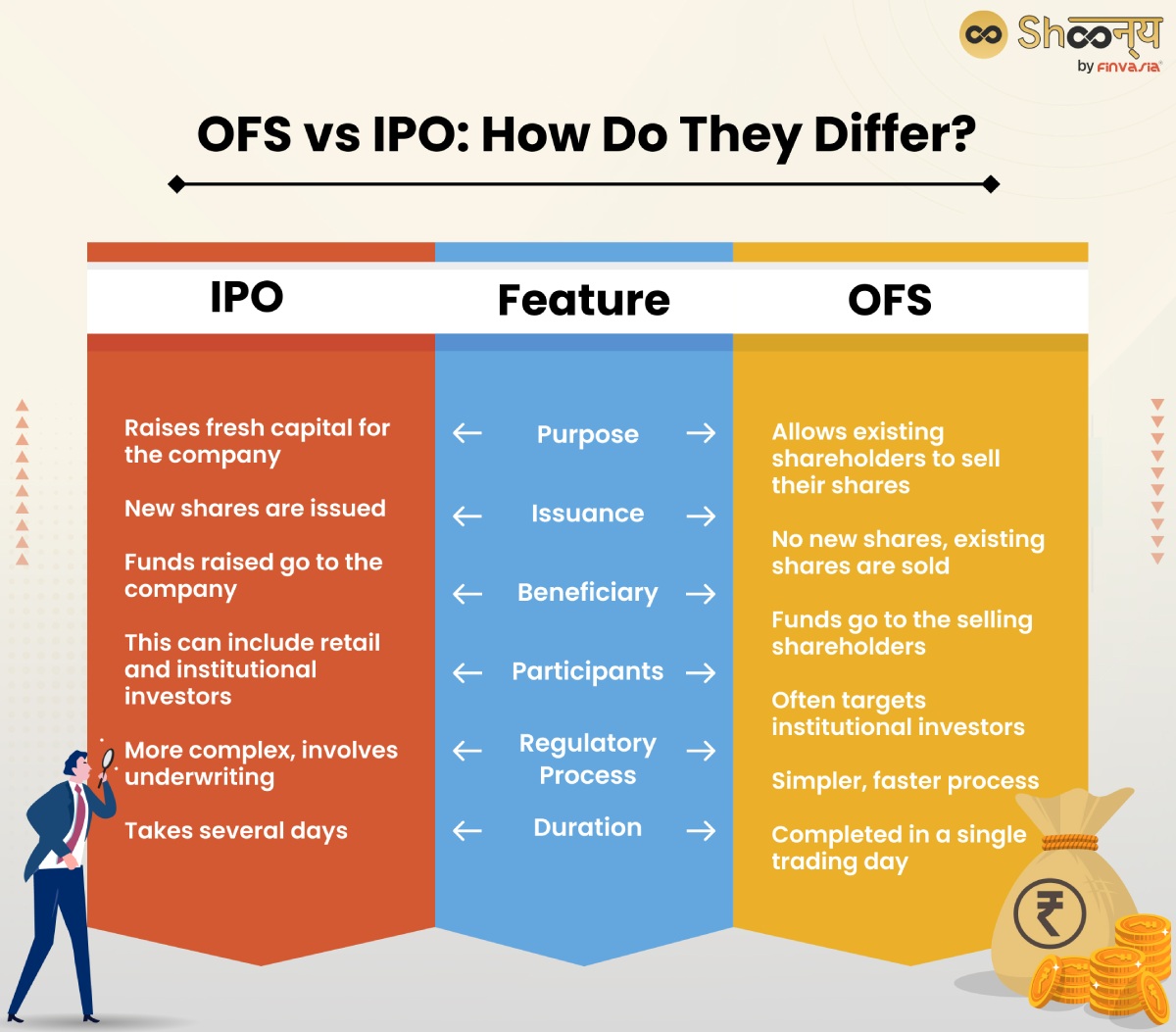
Here’s a table highlighting the differences between IPO and OFS:
| Basis of Differences | IPO | OFS |
| Nature | Fresh shares are created, allowing new investors to buy in. | Existing shares are sold by current shareholders. |
| Purpose | To raise funds for company growth, expansion, or debt repayment. | To allow shareholders to sell their shares and realize their investment. |
| Pricing | Prices are set through a bidding process, based on investor demand. | Prices are typically lower than market value to encourage quick sales. |
| Regulatory Process | Subject to strict SEBI regulations and detailed disclosures. | Simpler process with fewer regulations compared to IPOs. |
| Investor Accessibility | Open to all investors, promoting wider participation. | Often limited to specific groups like institutional investors. |
| Impact on Company’s Financial Structure | Changes the debt-to-equity ratio by adding new equity. | No direct effect on financial structure. |
| Time Frame | Longer preparation time due to complex requirements. | Quicker execution due to a more streamlined process. |
| Effect on Market Liquidity | Can increase liquidity by introducing new shares. | May or may not affect liquidity, depending on the scale of the sale. |
OFS vs IPO: Which is Better?
IPOs offer you the chance to be part of a potentially growing company from an early stage. On the other hand, OFS in share market provides you an opportunity to invest in a company with established market performance. When we talk about IPO vs OFS; both have merits and risks. The better option indeed depends on individual investment strategies and market conditions.
FAQs| OFS vs IPO
An IPO is a company’s first sale of stock to the public, an FPO is an additional stock issued by a public company, and an OFS is the sale of shares by existing shareholders.
One significant drawback of OFS is the limited control the seller has over the final share price. This is because the market demand and supply forces determine the price.
Investing in IPOs can be beneficial if the company has strong fundamentals and growth potential. However, it can also carry risks due to limited historical data and potential market volatility.
OFS stands for Offer for Sale, where existing shareholders sell their shares to the public during an IPO.
An Offer for Sale in an IPO allows current shareholders to sell their existing shares, rather than issuing new shares to raise capital.
OFS stands for “Offer for Sale” in stock market. This refers to the sale of existing shares by shareholders.
Source- sebi.gov.in
______________________________________________________________________________________
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks; read all the related documents carefully before investing.

