Do you get worried when you experience sudden market fluctuations and fear losing your investments or trades? Imagine starting a journey with a planned route, but market changes push you off track. Without adjustments, your portfolio could stray too far, risking unexpected challenges or missed opportunities. This is where portfolio rebalancing comes in.
If you are new to trading, here’s something you might want to know about: Portfolio Rebalancing. It guides investors back to their course, ensuring their strategy matches their goals and risk tolerance.
Now, what exactly is portfolio rebalancing, and why is it important? Let’s take a look!
What is Portfolio Rebalancing?
Portfolio rebalancing is a strategy that most traders use in the Indian stock market to adjust the mix of investments in their portfolios.
Let’s say you have some money invested in different types of stocks, like large companies and small companies. Over time, the value of these stocks can change.
Some might go up a lot, while others might not do as well.
Portfolio rebalancing means making changes to your investments to keep them in line with your original plan.
For example, if one type of stock now makes up more of your portfolio than you planned, you might sell some of it and buy more of the other types to get back to your target mix.
Thus, portfolio rebalancing is the process of realigning the weightings of assets in a portfolio. You can do this by buying or selling assets.
In simple terms, it’s like adjusting your investments to match what you originally decided based on your goals and risk tolerance. This helps manage risk and keeps your investments on track with your overall plan.
Now, how does the portfolio rebalancing actually work?
Let us take a look and understand it with an example.
How Portfolio Rebalancing Works
Portfolio rebalancing works by adjusting the allocation of investments in your portfolio.
Your main goal is to maintain your desired asset mix!
Here’s how it typically happens:
- Set Your Target Allocation: Begin by deciding on an ideal mix of investments based on your financial goals and risk tolerance.
For example, you might decide to distribute 70% of your portfolio to stocks and 30% to bonds.
- Monitor Your Portfolio: Regularly monitor your investments’ performance.
Over time, some investments may increase or decrease in value, causing your asset allocation to drift away from your target.
- Identify Rebalancing Trigger: Determine when to rebalance based on predetermined thresholds or time intervals.
For instance, you might rebalance annually or when a particular asset class deviates by more than 5% from your target allocation.
- Rebalance Your Portfolio: You can sell a part of the overperforming assets and use the proceeds to buy more of the underperforming assets.
This brings your portfolio back to its original asset allocation.
Portfolio Rebalancing Example
Let’s say you set up a portfolio with 50% invested in large-cap stocks (like HDFC Bank) and 50% in mid-cap stocks (like Titan Company).
Over time, due to market movements, the large-cap stocks perform well and now represent 60% of your portfolio. But, on the flipside, the mid-cap stocks make up only 40%.
To rebalance:
- Sell some of the large-cap stocks to bring their allocation back to 50%.
- Use the proceeds to purchase more mid-cap stocks, increasing their allocation back to 50%.
It’s important to note that the example provided is hypothetical. Actual portfolio decisions should be made based on thorough research and review of individual financial circumstances.
Different Types of Portfolio Rebalancing Strategies
Each of the following rebalancing strategies offers distinct advantages.
You can choose any of the portfolio rebalancing strategies depending on your investment goals. Additionally, you must also consider the level of involvement you wish in managing your portfolio.
1. Time-Based Rebalancing
Time-based rebalancing involves setting specific time intervals, such as quarterly or annually, to review and adjust portfolio allocation.
This means you could review your portfolio at predetermined intervals (e.g., every three months). Now, if the allocation has significantly deviated from the target, adopt reallocation.
- Example: If stocks now constitute 70% of the portfolio instead of the desired 60%, the investor sells some stocks to reallocate funds into other asset classes.
- Pros: Simple and systematic approach, consistent rebalancing schedule.
- Cons: Doesn’t consider market conditions or asset performance.
2. Constant Proportion Portfolio Insurance (CPPI)
It is a dynamic strategy that adjusts portfolio allocation based on market performance.
It involves combining elements of aggressive and conservative investing. This means allocating more to risky assets (like stocks) during market upswings. However, you must shift towards safer assets (like bonds) during downturns.
- Pros: Capitalizes on market trends and protects against significant market declines.
- Cons: More complex to implement, requires active management.
3. Percentage-of-Portfolio Rebalancing
It involves adjusting the portfolio when asset allocations deviate by a specified percentage from the target.
- Example: Let us say you began with the target of a 70/30 split. Now, if stocks drop to 64% and bonds increase to 46%, you must adopt rebalancing. You could sell bonds to buy more stocks and restore the original allocation.
- Pros: Offers flexibility in managing portfolio allocations.
- Cons: It may limit opportunities during market fluctuations.
Each rebalancing strategy requires careful consideration of individual investment objectives and market dynamics.
Importance of Rebalancing a Portfolio
Portfolio rebalancing is crucial for investors due to several reasons:
- Rebalancing ensures that risk levels are controlled by preventing overexposure to volatile asset classes during market fluctuations.
- It helps in adhering to the desired asset allocation strategy, aligning with long-term financial goals and risk appetite.
- It instils discipline in investment decisions, preventing emotional reactions to market movements. It helps you stick to a well-defined investment strategy
When Should You Consider Rebalancing Your Portfolio?
Investors should think about rebalancing their portfolio in common situations like these:
- Significant Market Changes: If there’s a big shift in the market that affects your investments, it’s a good time to rebalance to keep to your target mix.
- Regular Intervals: Many experts recommend rebalancing every six to twelve months to keep your portfolio in line with your goals.
- Major Life Events: Life changes like retiring, inheriting money, or a shift in income can alter your investment goals. Now, how much risk you’re comfortable with leads to a rebalance.
- Change in Risk Tolerance: If your comfort level with risk changes, you might need to adjust your portfolio to match.
- Shift in Financial Goals: If your financial goals change, rebalancing can help you adjust your investments to fit your new plans.
Five Simple Steps for Effective Portfolio Rebalancing
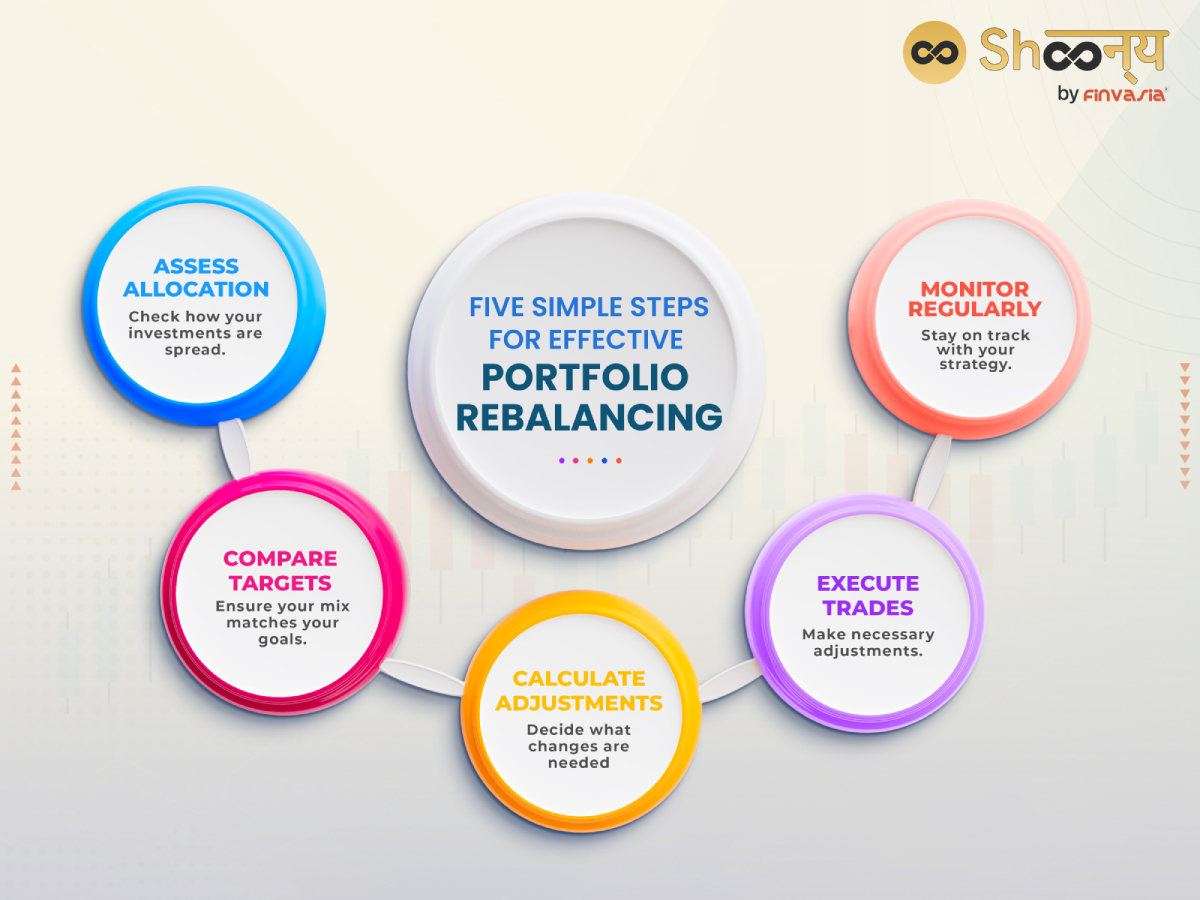
- Assess Your Current Allocation
Review how your investments are distributed across different types (stocks, bonds, etc.).
- Compare with Your Target Allocation
Check if your current allocation matches your desired investment mix.
- Calculate Adjustments Needed
Identify which assets need to be adjusted (bought or sold) to reach your target allocation.
- Make the Necessary Trades
Execute the trades needed to rebalance your portfolio.
- Monitor and Repeat
Regularly review and adjust your portfolio to maintain your investment strategy.
Pros and Cons of Portfolio Rebalancing
| Pros | Cons |
| Helps maintain desired risk-return profile. | Incurs transaction costs. |
| Limits exposure to overperforming assets. | Requires regular monitoring and decision-making. |
| Disciplined approach to long-term investing. | It may involve tax implications upon selling assets. |
| Can enhance diversification. | Potential to miss out on short-term gains. |
Conclusion
Portfolio rebalancing is a strategic practice vital for maintaining desired asset allocations. By periodically adjusting holdings to restore intended proportions it helps you optimise returns while staying resilient to market fluctuations.
FAQs| Portfolio Rebalancing
Rebalancing your portfolio helps maintain your desired risk level and diversification, although it may impact tax strategies.
You must Check and review your portfolio regularly. You can do it monthly or at least once a year to ensure everything is in line with your goals.
Regularly checking and adjusting your investments ensures they match your risk tolerance and financial goals.
A balanced portfolio spreads risk across various assets and offers stability during market ups and downs.
______________________________________________________________________________________
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks; read all the related documents carefully before investing.

